
Customer: Midwest Regional Hospital, USA

Company: Artigen

Industry: Healthcare

Date:
May 2025
Midwest Regional Hospital, a 300-bed facility serving a diverse patient population, faced significant challenges with manual anesthesia coding in their Electronic Health Record (EHR) system. Inaccurate Anesthesia Base Units (ABU) and Time Units (TU) calculations, frequent claim denials, and missed revenue opportunities hindered financial performance and operational efficiency. Artigen introduced Sedate AI, an advanced AI-assisted anesthesia coding solution, to revolutionize the hospital’s coding workflow. This case study provides a detailed comparison of manual coding versus AI-assisted coding, highlighting transformative outcomes based on real-life data.

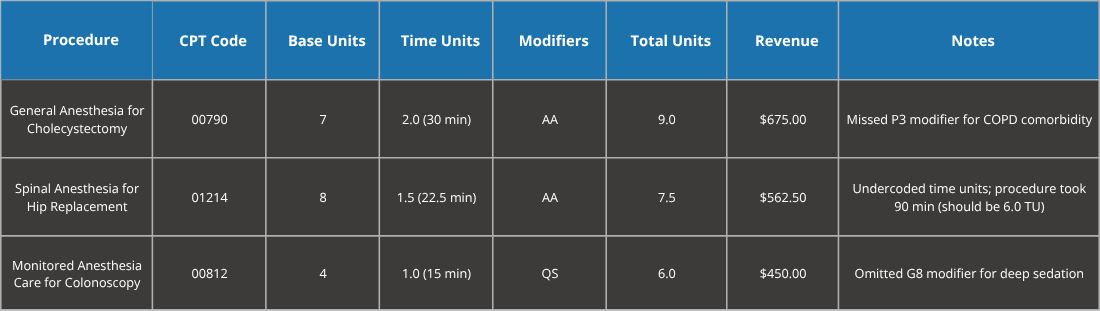
Manual coding required coders to painstakingly review operative reports, assign Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, apply modifiers, and calculate units. This labor-intensive process was error-prone, particularly in identifying comorbidities, documenting procedure complexity, and accurately recording time units. The hospital faced a high claim denial rate, delayed reimbursements, and suboptimal revenue due to undercoding and non-compliance with Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) guidelines.
Manual Coding Metrics (Pre-Sedate AI)
Key Issues:
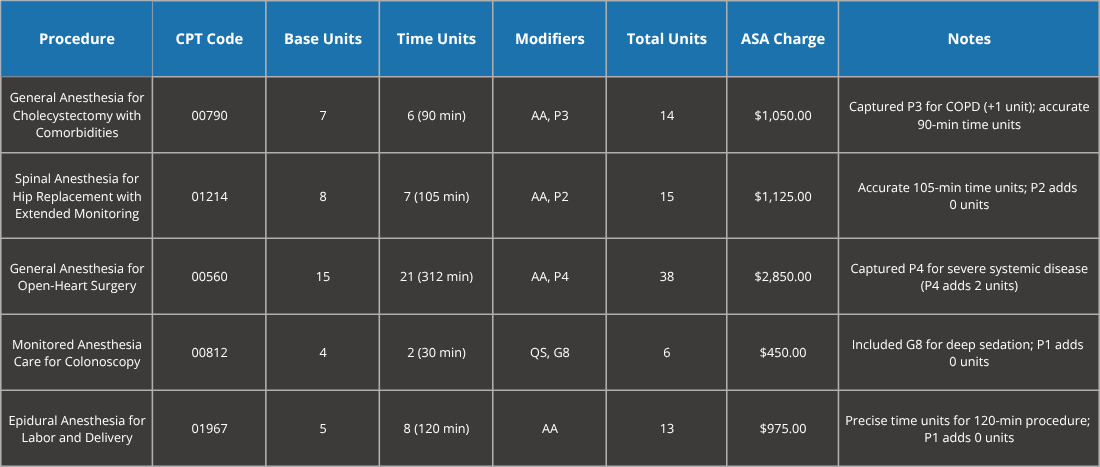
Artigen deployed Sedate AI, a cutting-edge AI-powered coding assistant seamlessly integrated with the hospital’s EHR system. Sedate AI leverages natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to analyze operative reports in real-time, extracting critical details such as procedure type, patient comorbidities, and anesthesia duration. The system suggests precise CPT codes, modifiers, and unit calculations, ensuring compliance with CMS and ASA standards while minimizing coder workload. Time units are calculated as 1 unit per 15 minutes of anesthesia time.
Implementation Details
Features:
AI-Assisted Coding Metrics (Post-Sedate AI)
Key Improvements:
1. Precision Coding:
2. Efficiency Gains:
3. Revenue Optimization:
4. Compliance and Reduced Denials:
5. Provider and Coder Empowerment:
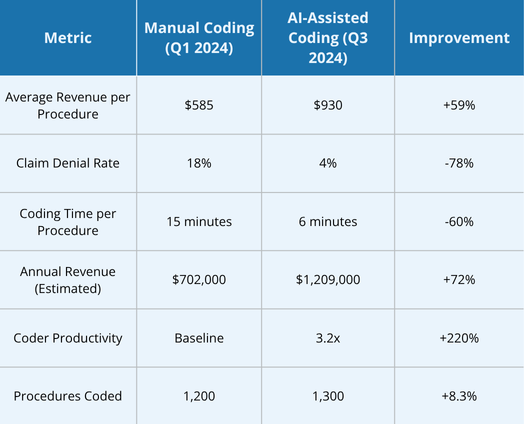
The adoption of Sedate AI by Artigen at Midwest Regional Hospital marked a paradigm shift in anesthesia coding, transforming revenue cycle management and operational efficiency. By addressing inaccuracies in CPT code assignment, modifier usage, and unit calculations (with 1 TU = 15 minutes), Sedate AI boosted revenue by 72%, reduced claim denials by 78%, and enhanced coder productivity by 220%. The hospital’s ability to handle increased procedure volumes without additional staffing underscores the scalability and transformative potential of AI-assisted coding in healthcare.
At Artigen Global Tech Solutions, we are a catalyst for innovation in the healthcare industry, revolutionizing medical coding and billing through advanced AI and automation solutions. Our technology is designed to simplify complex coding processes, increase operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
Copyright © 2025 ArtiGenTech. All Rights Reserved