
Customer: Coastal Community Hospital, USA

Company: Artigen

Industry: Healthcare

Date:
May 2025

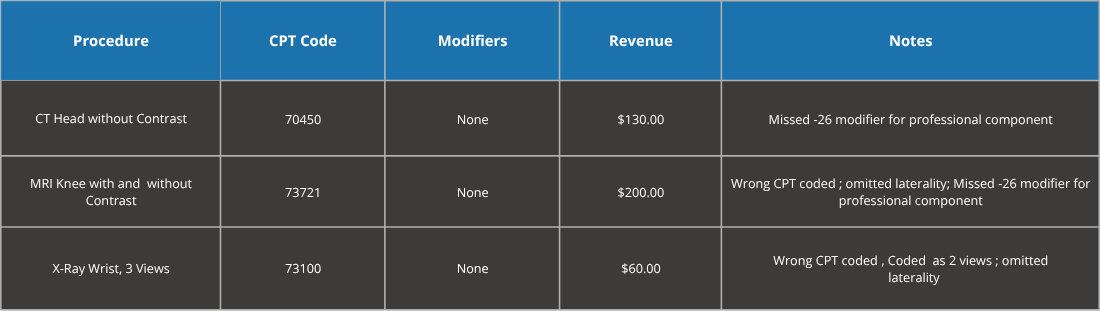
Manual radiology coding involved coders manually reviewing imaging reports to assign CPT codes, modifiers, and ensure payer compliance. Unlike anesthesia coding, radiology coding focuses on imaging modalities, anatomical specificity, and technical/professional components rather than time units or patient physical status. The process was error-prone, particularly in documenting contrast use, laterality, and multi-region studies. Coastal Community Hospital faced high claim denial rates, undercoding, and non-compliance with Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and American College of Radiology (ACR) guidelines, resulting in financial and operational inefficiencies.
Manual Coding Metrics (Pre-Conrad AI)
Key Issues:
Artigen introduced Conrad, a cutting-edge AI-powered coding assistant tailored for radiology and integrated with the hospital’s EHR system. Unlike anesthesia coding, which emphasizes time-based units and patient comorbidities, Conrad focuses on imaging-specific details, such as modality, contrast administration, and anatomical precision. Using natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, Conrad analyzes radiology reports in real-time, extracting details like imaging type, region, and clinical indications to suggest accurate CPT codes, modifiers, and documentation requirements, ensuring compliance with CMS and ACR standards.
Implementation Details
Features:
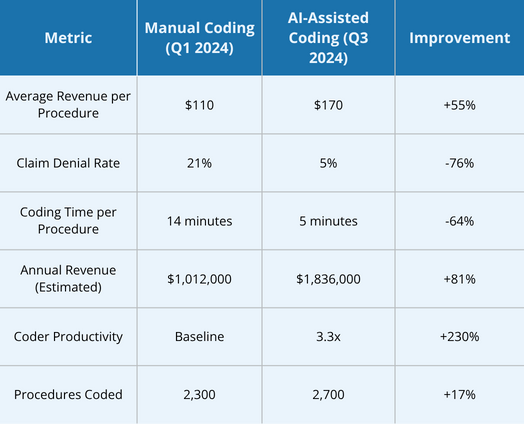
AI-Assisted Coding Metrics (Post-Conrad)
Key Improvements:

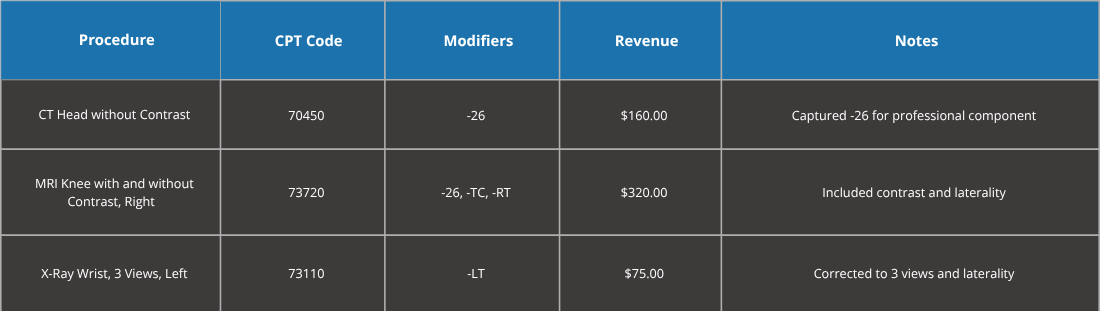
1. Precision Coding:
2. Efficiency Gains:
3. Revenue Optimization:
4. Provider and Coder Empowerment:
The deployment of Conrad by Artigen at Coastal Community Hospital transformed radiology coding, delivering precision, efficiency, and revenue optimization distinct from anesthesia coding challenges. By addressing inaccuracies in CPT code assignment, modifier usage, and documentation specific to imaging studies, Conrad increased average revenue per procedure by 55%, reduced claim denials by 76%, and tripled coder productivity. The ability to close coding gaps in under 5 minutes per patient streamlined operations, reduced administrative burden, and empowered radiologists to prioritize diagnostic excellence. This case study highlights the transformative potential of AI-driven coding in radiology billing, establishing a benchmark for healthcare providers seeking financial and operational excellence.
At Artigen Global Tech Solutions, we are a catalyst for innovation in the healthcare industry, revolutionizing medical coding and billing through advanced AI and automation solutions. Our technology is designed to simplify complex coding processes, increase operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
Copyright © 2025 ArtiGenTech. All Rights Reserved